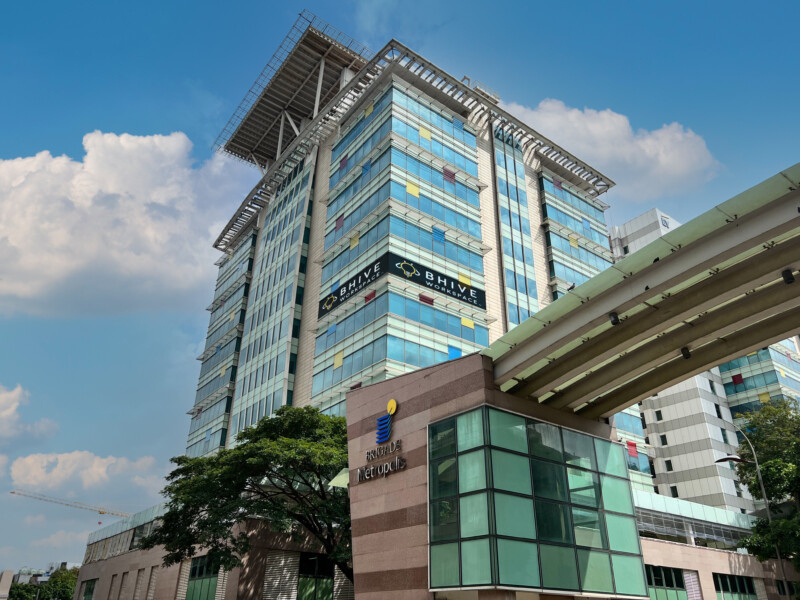
Welcome to the future of India’s Commercial Real Estate!

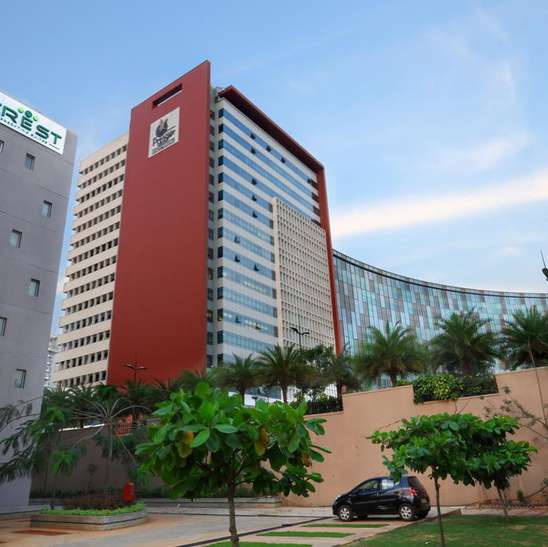
Constructed by Brigade Group

Grade-A OC Certified Building

Sales Deed and Khata provided to the buyer

BMRCL Metro Station in front of Brigade Metropolis

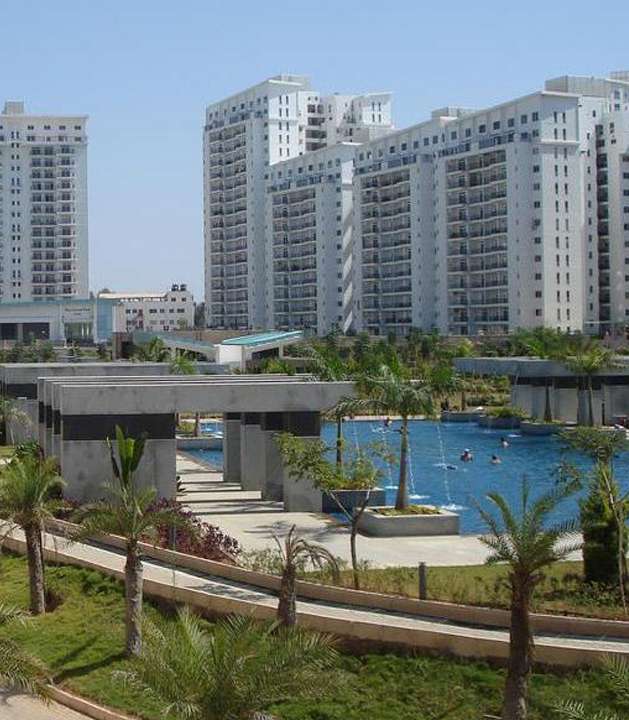
Marquee Asset in Mahadevapura, Whitefield

Constructed by Brigade Group

Grade-A OC Certified Building

Sales Deed and Khata provided to the buyer

BMRCL Metro Station in front of Brigade Metropolis

Marquee Asset in Mahadevapura, Whitefield

10.6% *
Gross Avg Rentals (p.a)
22,940 sq.ft
Super built-up area*

15 Years
Lease term

21 Units
of Inventory available
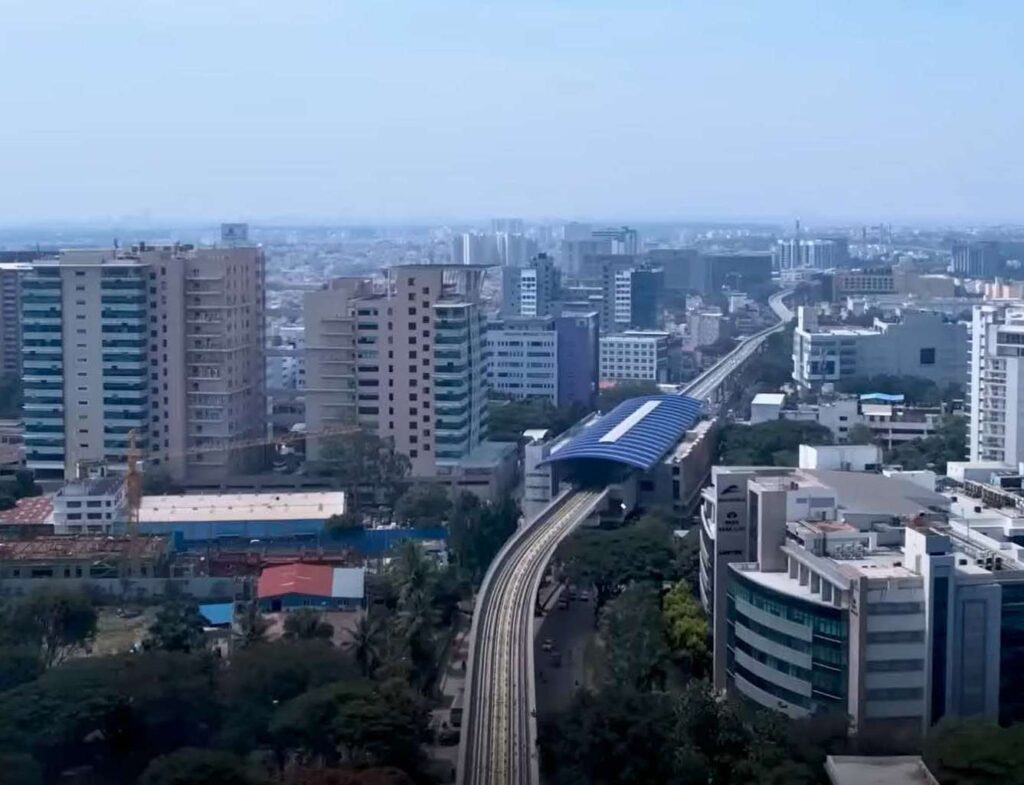






Bengaluru International Airport 41 Km

Central Business District 10 Km

Premium Residential Societies

Multiple Metro Access - Purple line

Multi Cuisine Restaurants & 5-star Hotels
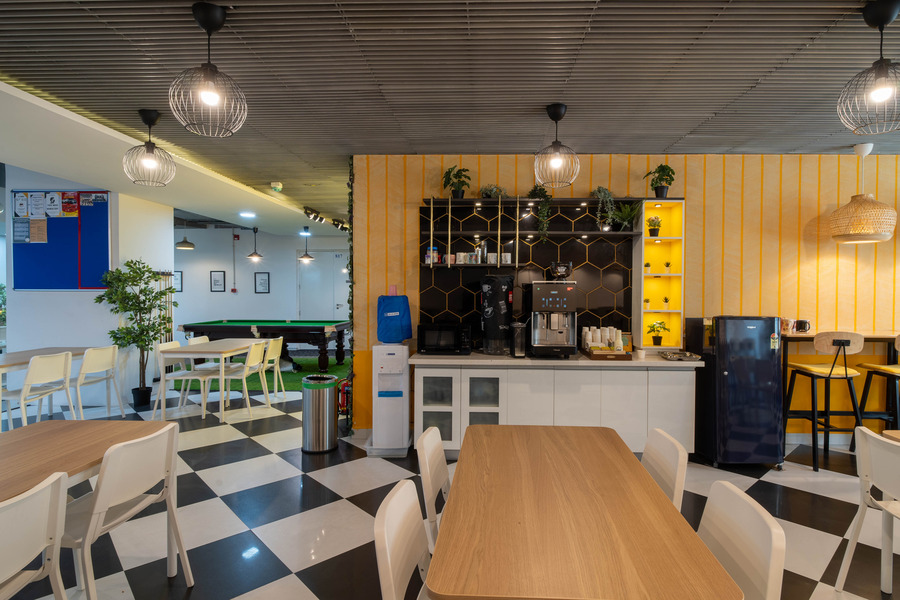
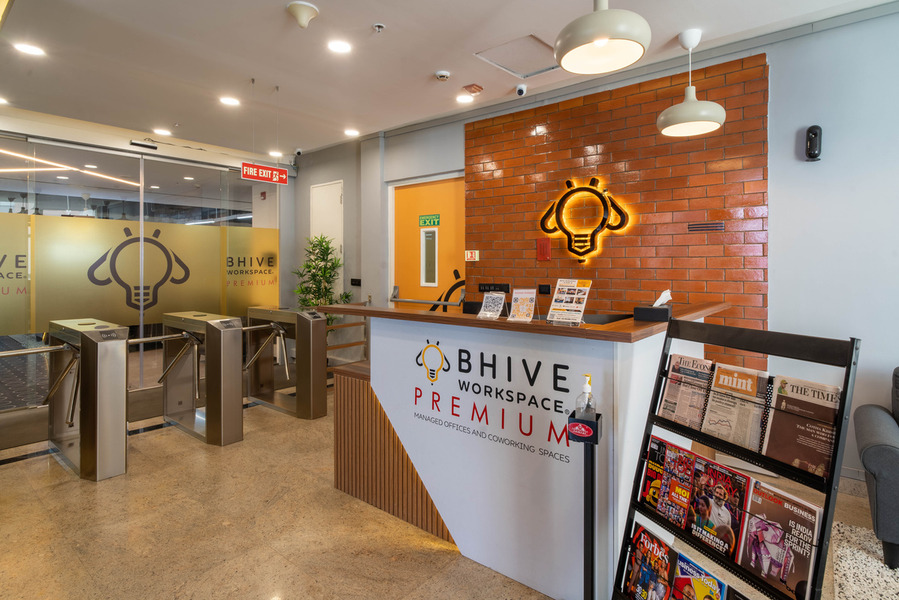
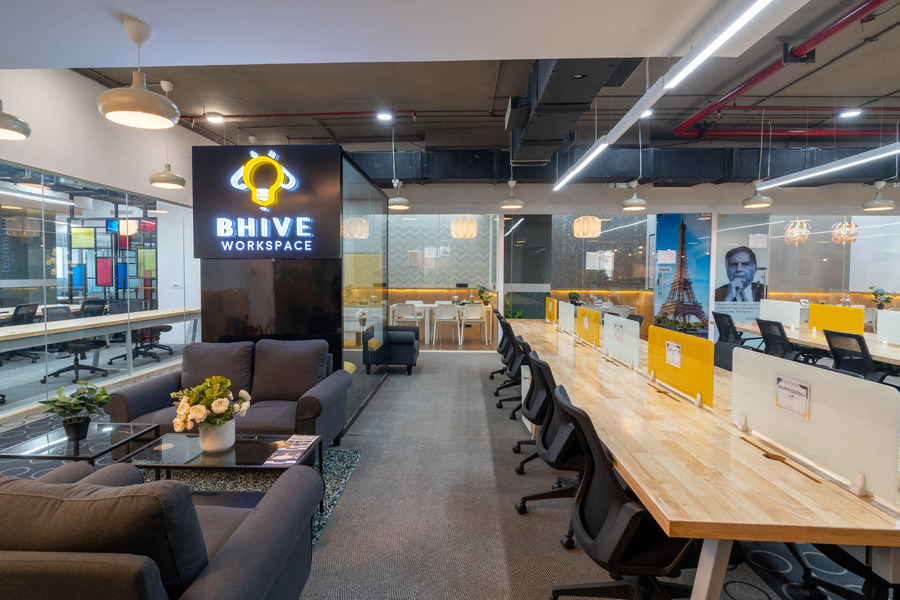




Contact Us
©2024 Venturelord SpaceTech Pvt. Ltd


Bengaluru, Karnataka

Bengaluru, Karnataka